Lyme disease has been found to have an impact on dental health, particularly due to the presence of spirochetes, the bacteria that cause Lyme disease, in the oral cavity. These spirochetes can affect the gums and teeth, leading to oral health issues such as chronic periodontitis. When the oral pH is low, creating an acidic environment, it can contribute to the growth of spirochetes in the gums, leading to inflammation and potential damage to the tissues supporting the teeth.
Furthermore, studies have shown that Lyme bacteria can be present in root canal treated teeth, posing a potential risk to oral health. This highlights the importance of testing root canal treated teeth for spirochetes and other pathogens to ensure that the oral environment remains healthy and free from harmful bacteria.
Chronic periodontitis, a condition characterized by inflammation and infection of the gums, can result in symptoms such as swollen and bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and loose teeth. It is important for individuals with Lyme disease to be aware of the potential impact on their dental health and to work with their healthcare providers to address any oral health concerns that may arise.
There are three phases of general clinical manifestations
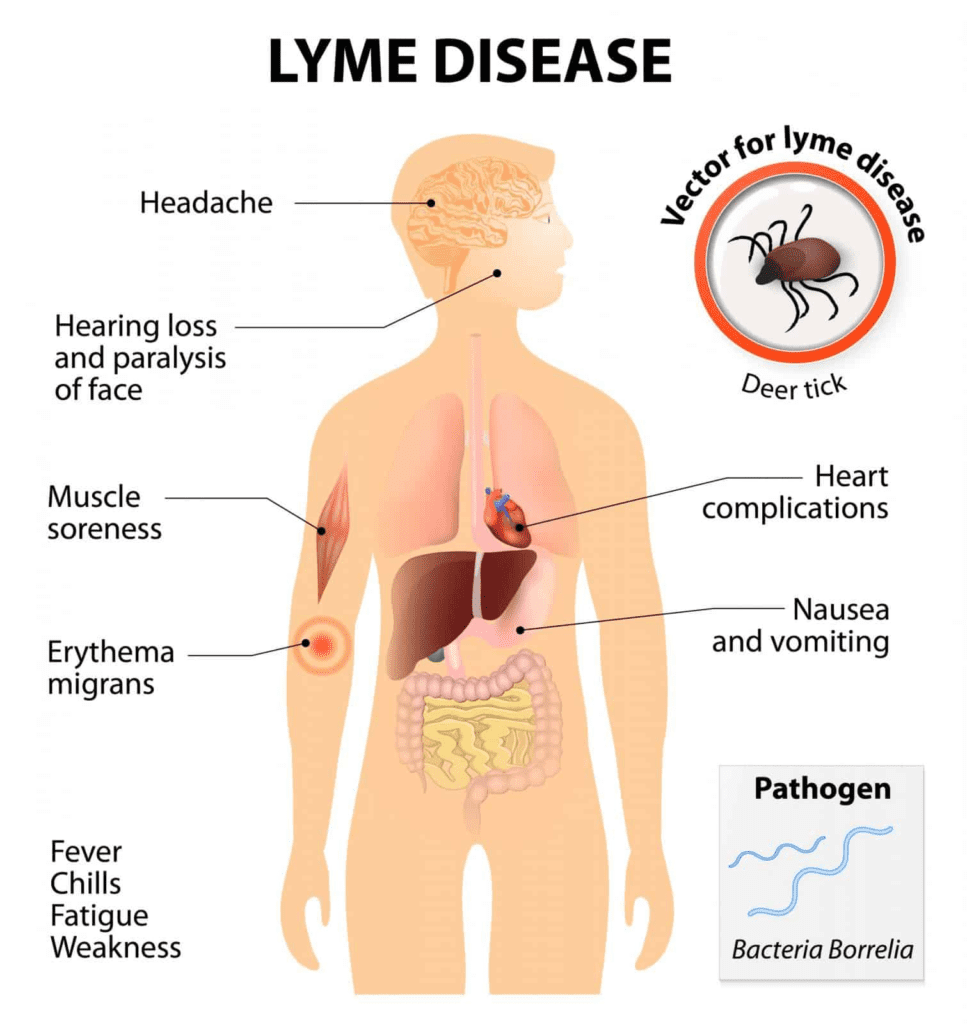
Lyme disease has three phases of general clinical manifestations: early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated. In the early localized phase, the most common symptom is a red, expanding rash called erythema migrans. This phase may also present with flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, headache, and muscle and joint aches.
The early disseminated phase can occur weeks to months after the initial infection and may include symptoms such as multiple skin rashes, facial paralysis, meningitis, and heart palpitations. In the late disseminated phase, arthritis, neurological symptoms, and cognitive difficulties may develop.
Early detection and treatment of Lyme disease are crucial, as the infection can spread to different body systems and lead to more severe symptoms. Prompt antibiotic therapy in the early stages can prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Does Lyme disease affect teeth?
Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, can lead to a variety of dental problems, including temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ) and facial pain. The bacteria can affect the muscles and ligaments in the jaw, leading to TMJ disorder, which can result in jaw pain, difficulty with jaw movement, and even dental misalignment. Additionally, Lyme disease can cause facial nerve inflammation, resulting in facial pain and discomfort.
Some potential symptoms of Lyme disease impacting oral health include jaw pain, difficulty chewing or swallowing, facial numbness, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss. The impact of Lyme disease on oral health can be significant, potentially leading to chronic pain, difficulty with daily activities such as eating and speaking, and overall decreased quality of life.
It is important for individuals with Lyme disease to be aware of the potential impact on their oral health and seek dental care to address any related issues. Additionally, proper management and treatment of Lyme disease are crucial in minimizing its impact on oral health.
Tooth extractions and Lyme disease
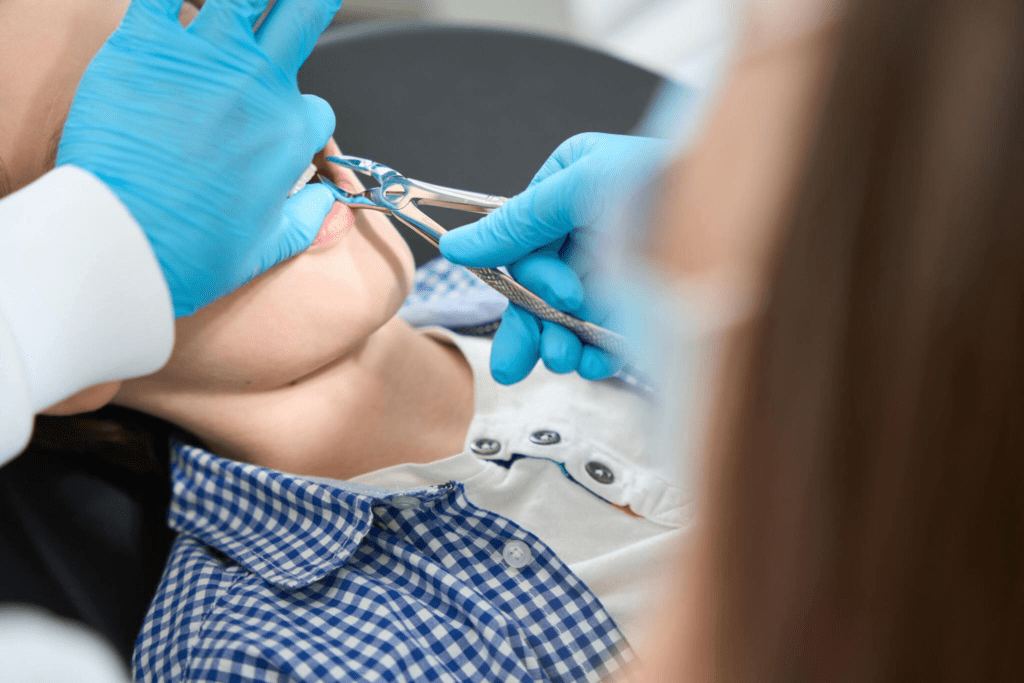
Lyme disease can have potential impacts on dental health, especially in relation to tooth extractions and gum problems.
During a tooth extraction, there is a possibility that Borrelia germs, which cause Lyme disease, can be exposed. This poses a risk for individuals with Lyme disease as it can lead to the spread of the infection and exacerbate the symptoms. Additionally, there is a connection between Lyme disease and temporomandibular joint dysfunction, which can cause pain and discomfort in the jaw.
Furthermore, Lyme disease can also affect gum health, leading to gum problems such as inflammation and periodontal disease. This can impact oral health by causing gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss if left untreated. It’s important for individuals with Lyme disease to be aware of these potential dental issues and to work closely with their dental and healthcare providers to address and manage any related concerns.
Is it possible for Lyme disease to impact the mouth?
Lyme disease can have a potential impact on oral health, leading to symptoms such as dry mouth, inflammation of the pulp, and burning mouth syndrome. These oral symptoms can be related to neurological issues caused by the bacteria, as Lyme disease can affect the central nervous system and lead to nerve damage and dysfunction.
The ways in which Lyme disease can affect the mouth include dry mouth, changes in taste, and difficulty swallowing. Inflammation of the pulp, known as pulpitis, can occur, causing tooth sensitivity and pain. Burning mouth syndrome, characterized by a burning or tingling sensation in the mouth, can also be a symptom of Lyme disease.
Overall, Lyme disease can lead to a range of oral health issues that can impact a person’s quality of life. It is important for individuals with this disease to be aware of these potential oral symptoms and seek appropriate dental care to manage them.
Common oral symptoms
Oral symptoms of Lyme disease that can mimic dental pathology include dry mouth, tooth sensitivity, pulpitis, pain in the chewing muscles, and TMJ pain. These symptoms can easily be mistaken for typical dental issues, leading to misdiagnosis in the dental setting. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial because misdiagnosis can delay proper treatment for Lyme disease, allowing the infection to progress and potentially lead to more severe health complications.
Lyme bacteria can be present in the mouth and contribute to these oral symptoms. The bacteria can directly infect the oral tissues, causing inflammation and pain. Additionally, the systemic effects of Lyme disease, such as immune system dysregulation and inflammation, can also manifest as oral symptoms. Therefore, dental healthcare providers should be vigilant in considering Lyme disease as a potential cause of oral symptoms that do not respond to typical dental treatments.
What is the solution to this issue?
At Wellness Dental, we specialize in providing holistic dental treatment, including ozone therapy and other minimally invasive procedures. If you have concerns about Lyme disease and its impact on oral health, we encourage you to schedule an appointment and our dental team.
During your appointment, we will discuss the connection between wellness and oral health to ensure a comprehensive approach to your overall well-being. We understand the importance of addressing underlying health issues, such as Lyme disease, and their potential impact on your oral health.
Our goal is to provide personalized and comprehensive care that takes into account your individual needs and concerns. We believe in a proactive and integrative approach to dental health that includes addressing any systemic health issues that may affect your oral health.
Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards achieving optimal oral and overall health. Let us help you address your concerns about Lyme disease and explore holistic dental treatment options that can benefit your wellness.
FAQ
Can Lyme disease cause teeth problems?
Lyme disease, a bacterial infection transmitted through tick bites, can indeed cause teeth problems. The impact of Lyme disease on oral health is often overlooked, but it can have significant consequences. Oral symptoms associated with Lyme disease include dry mouth, changes in taste, and difficulty swallowing. One common dental issue caused by Lyme disease is inflammation of the pulp, known as pulpitis. This can lead to tooth sensitivity and pain.
What are the 4 late symptoms of Lyme disease?
Late symptoms of Lyme disease can vary from person to person, but there are several common manifestations that can occur. One late symptom is joint pain, which can affect various joints in the body and lead to stiffness and limited range of motion. This joint pain can be persistent and worsen over time if left untreated.
Another late symptom of Lyme disease is muscle pain, which can also be chronic and debilitating. Individuals may experience muscle aches, cramps, and weakness, making it difficult to engage in regular
What’s the worst that can happen with Lyme disease?
The worst that can happen with Lyme disease is the progression of the infection and the potential for severe health complications. If left untreated or misdiagnosed, Lyme disease can lead to long-term damage to various systems in the body.
One potential consequence of Lyme disease is the development of neurological symptoms. This can include facial nerve palsy, which can cause weakness or paralysis on one side of the face. The inflammation caused by the infection can affect the facial nerve, leading to this condition.
What are the lingering effects of Lyme disease?
The lingering effects of Lyme disease can vary from person to person, but they can have a significant impact on overall health and well-being. One common lingering effect is joint pain, which can manifest as persistent discomfort, stiffness, and limited range of motion in the joints. This joint pain can make it difficult to engage in regular activities and may worsen over time if left untreated.






