What is a Crossbite?
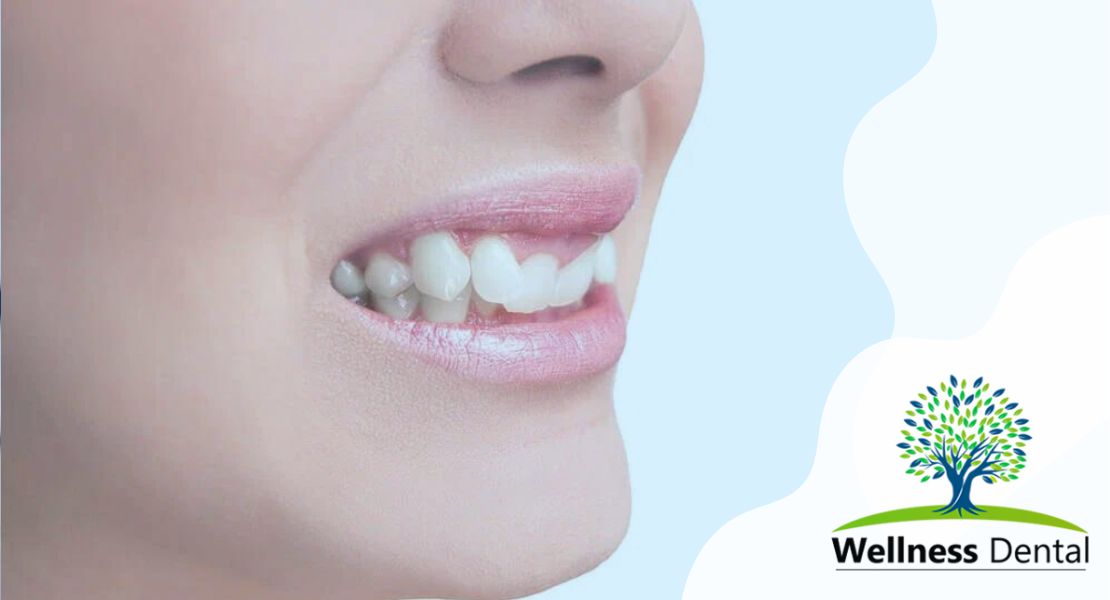
A crossbite is a type of malocclusion where one or more teeth on the upper jaw are positioned behind the corresponding teeth on the lower jaw. This dental condition can affect anyone, regardless of age. Patients with crossbites may experience crowded teeth, misaligned teeth, gum recession, tooth decay, jaw pain, and facial asymmetry.
A crossbite can be caused by childhood habits such as thumbsucking, tongue-thrusting, and mouth breathing. It can also be due to uneven jaw growth or facial features that affect dental alignment. If left untreated, a crossbite can result in pain, tooth loss, and further oral health problems.
There are different types of crossbites, including posterior crossbites where the upper teeth at the back of the mouth are affected, and anterior crossbites where the lower front teeth are positioned in front of the upper teeth. Fortunately, crossbites are treatable with orthodontic treatment, which includes orthodontic devices such as palate expanders, traditional braces, and removable expanders.
In some cases, jaw surgery may be necessary to fix severe crossbites. A qualified pediatric dentist or orthodontist can assess the severity of the crossbite and create a personalized treatment plan that will correct the misaligned teeth and promote a healthy bite.
Signs and Symptoms of a Crossbite
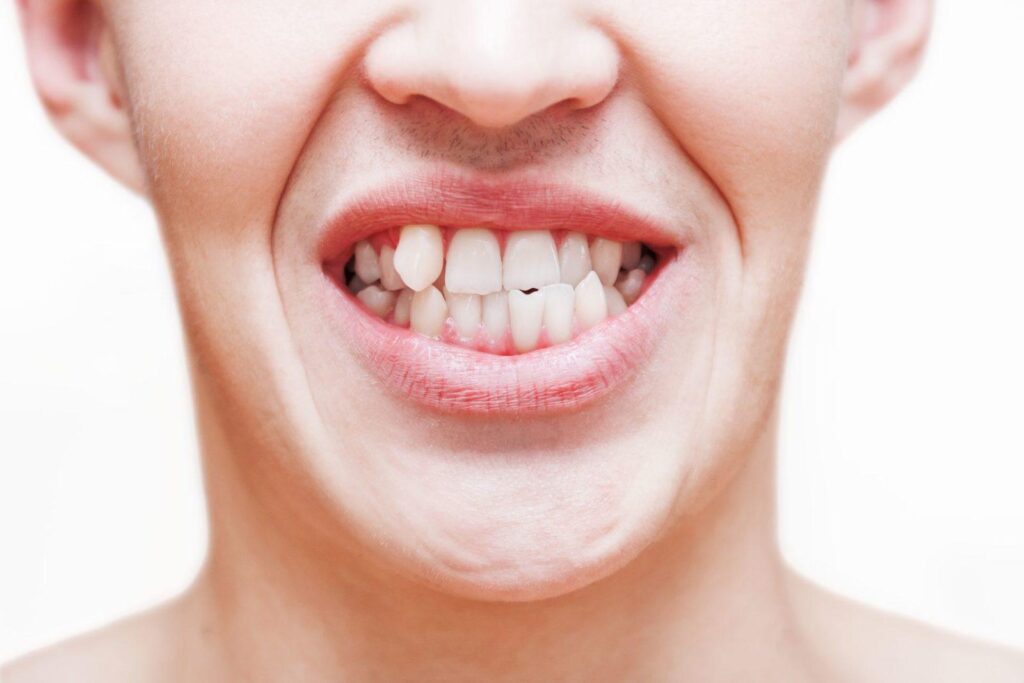

A crossbite is a type of malocclusion where the upper teeth rest inside the lower teeth when biting down. If left untreated, it can lead to various signs and symptoms. One of the most common signs is difficulty biting or chewing. This is because the biting force is unevenly distributed, and the molars may not be able to grind food properly.
Another common symptom is mouth breathing, which can lead to dry mouth and increased risk of tooth decay. A crossbite may also cause jaw pain, particularly in the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), resulting in headaches and neck pain. Speech problems may also be observed due to the improper position of the teeth.
A crossbite can also affect facial development, especially in children. It can lead to uneven jaw growth or facial asymmetry. Furthermore, the repetitive movements of the jaw in a crossbite can lead to teeth grinding and wear, resulting in weakened teeth and gum recession.
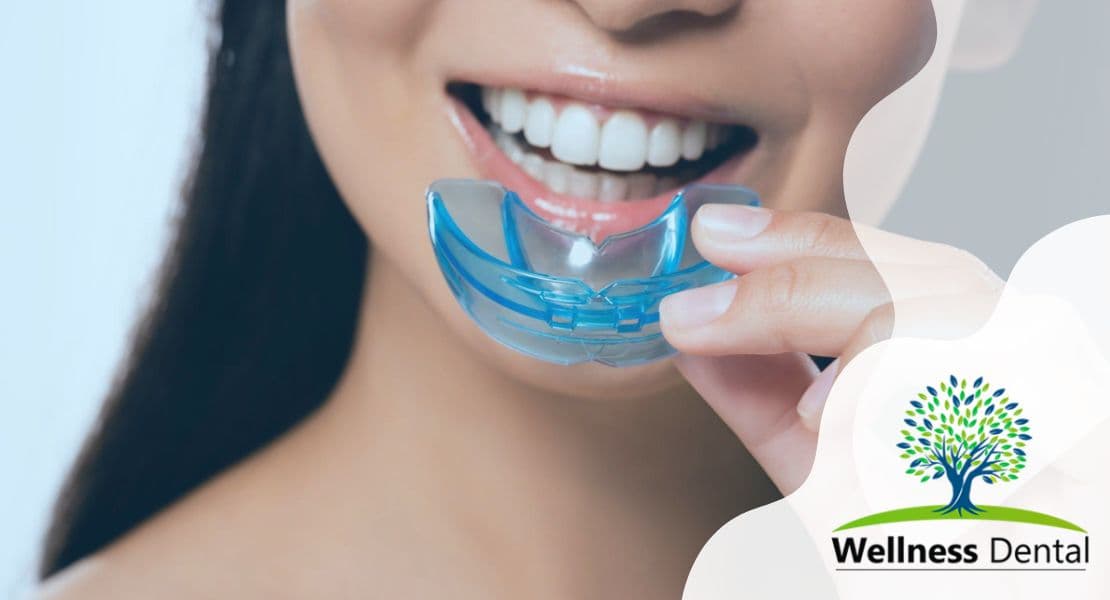
If you are experiencing any of these signs and symptoms, it is essential to seek treatment for a crossbite. Your orthodontic treatment plan may involve the use of orthodontic devices such as traditional braces, palatal expanders, or removable expanders, depending on the severity of the crossbite. With proper treatment, you can achieve a healthy bite and a beautiful smile.
Diagnosis of a Crossbite
Diagnosis of a crossbite is crucial in determining the best course of treatment for correcting this malocclusion. During a routine dental check-up, a dentist can diagnose a crossbite by examining the position of the teeth and how they come together when the mouth is closed. They may also take X-rays or impressions of the teeth to get a better understanding of the issue.
Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or a palatal expander, may be required to correct a crossbite. In some severe cases, jaw surgery may be necessary. Timely diagnosis and treatment of a crossbite can not only improve oral health but also prevent potential facial asymmetry and jaw pain in the long term.
Examining the Mouth for Signs of a Crossbite
Identifying a crossbite requires a thorough examination of the mouth. The first sign to look for is a misalignment of the upper and lower teeth. If the upper teeth are positioned inside the lower teeth when the mouth is closed, a posterior crossbite may be present. A palatal expander may be used to widen the upper jaw to correct this condition.
Another sign to look for is trouble closing the mouth completely. A crossbite can cause difficulty in fully closing the mouth, as it can prevent the teeth from meeting in the correct position. Lisping and other speech difficulties may also be present due to the misalignment of the teeth.
Cheek and lip biting may also occur due to the improper occlusion of teeth. In some cases, a single tooth may stick out due to the crossbite and create an imbalanced bite. The goal of crossbite treatment is to correct the misalignment and achieve a healthy bite.
In summary, a crossbite examination includes observing for teeth misalignment, speech difficulties, lip biting, and difficulty closing the mouth. If a crossbite is suspected, it’s essential to consult an orthodontic specialist to develop a treatment plan for proper correction.
X-rays and Other Imaging Tests
When diagnosing a crossbite, X-rays and other imaging tests play an important role in determining the extent of the misalignment. X-rays help to provide a clear and detailed picture of the teeth and jaw, allowing orthodontists to assess the alignment and position of individual teeth and identify any underlying abnormalities that may be contributing to the crossbite.
In addition to X-rays, other imaging tests such as CT scans and MRI can also be helpful in detecting any jaw or teeth abnormalities that may be present. These tests can provide more detailed information about the structure of the jaw, the position of the teeth, and the overall health of the oral cavity.
Overall, X-rays and other imaging tests are essential tools for orthodontists in diagnosing and treating crossbites. By providing a clearer picture of the teeth and jaw, these tests help orthodontists to develop a more accurate diagnosis and treatment plan, ensuring that patients receive the most effective and appropriate care for their specific needs.
Types of Crossbites
Crossbite is one of the most common malocclusions affecting both children and adults. It occurs when the upper and lower teeth do not come together in their correct position, usually due to uneven jaw or teeth growth. Crossbites can negatively impact oral health and facial features, which is why early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential.
There are three types of crossbites: anterior, posterior, and lateral, each having unique characteristics, causes, and treatments. Understanding the types of crossbites can help patients and their families make informed decisions regarding their orthodontic treatment plan. In this article, we will discuss the different types of crossbites in detail, their symptoms, causes, and treatment options.
Anterior (Front) Crossbite
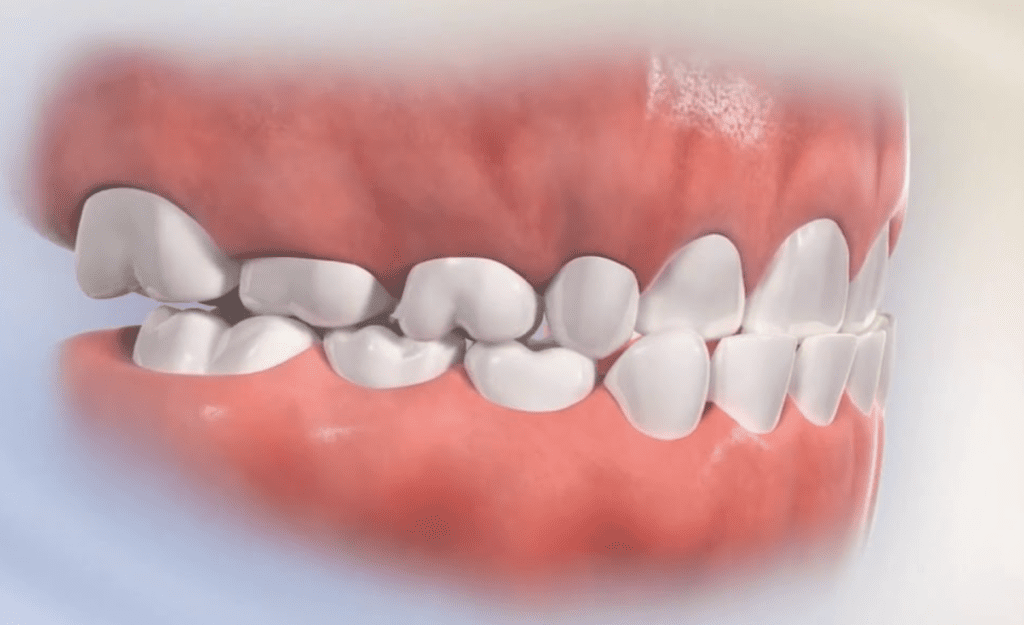
An anterior crossbite occurs when the upper front teeth rest behind the lower front teeth instead of in front of them, resulting in a misaligned bite. Unlike a posterior crossbite which affects the back teeth, the anterior crossbite focuses purely on the front teeth and does not involve any jaw problems.
This type of crossbite can lead to various issues such as difficulty speaking, biting or chewing, and even jaw pain. It can also cause excessive wear or chipping of the teeth, and increase the risk of developing gum disease, tooth decay, and gum recession.
Various factors can cause an anterior crossbite, including genetic factors, a shortened upper jaw, or childhood habits such as thumb sucking. Early detection and treatment of the crossbite can prevent further complications in the future.
Treatment options include orthodontic appliances and traditional braces, orthodontic devices such as rubber bands, and even surgery in severe cases. It is essential to maintain good oral hygiene during treatment to minimize the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. Correcting an anterior crossbite not only improves oral health but also enhances facial features and creates a more confident and beautiful smile.
Posterior (Back) Crossbite
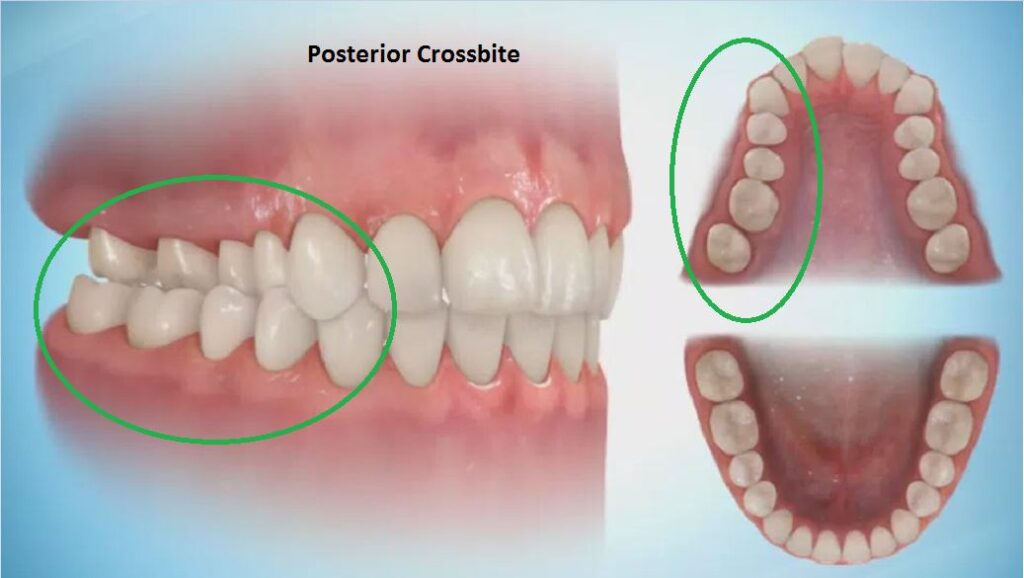
A posterior crossbite occurs when the upper back teeth bite inside of the lower back teeth. It can cause dental and skeletal problems if left untreated. Dental problems may include tooth decay, gum disease, and tooth wear. Also, skeletal problems can arise, such as uneven jaw growth, facial asymmetry, and neck pain.
Delayed loss of baby teeth and long-term pacifier use are common causes of posterior crossbite. When baby teeth stay in for a longer period, it can cause permanent teeth to erupt in the wrong position. Similarly, long-term use of pacifiers can affect the development of the jaw and teeth.
Fortunately, there are multiple treatments available for posterior crossbite correction, including orthodontic treatment with braces or Invisalign®️. Braces can be used to move teeth into the proper position, and Invisalign clear aligners can also be used for minor cases of posterior crossbite. In severe cases, jaw surgery may be required to fix the problem.
It is important to seek treatment for posterior crossbite to avoid dental problems and improve overall oral and skeletal health. Orthodontic treatment for posterior crossbite should be carried out by a professional pediatric dentist to maximize results.
Double or Multiple Crossbites
Double or multiple crossbites occur when several teeth are in crossbite at the same time. This type of malocclusion can result from a narrow lower jaw or a wide upper jaw. Double or multiple crossbites can cause uneven wear on teeth, gum recession, tooth decay, and jaw pain.
There are two types of double or multiple crossbites: anterior and posterior.
Anterior double or multiple crossbites occur when the upper front teeth bite inside the lower front teeth. Posterior double or multiple crossbites occur when the upper back teeth bite inside the lower back teeth.
Treatment for double or multiple crossbites depends on the severity and cause of the malocclusion. In mild cases, orthodontic treatment with braces or Invisalign clear aligners can correct the problem by moving teeth into their proper position. In more severe cases, orthodontic devices such as a palatal expander or rubber bands may be used to widen the upper jaw or narrow the lower jaw. In extreme cases, jaw surgery may be necessary to fix the misalignment.
If left untreated, double or multiple crossbites can lead to more serious dental and medical issues. It’s crucial to seek treatment from a qualified orthodontist or pediatric dentist to achieve a healthy bite and prevent future complications.
Causes of a Crossbite
A crossbite is a dental condition where the teeth in the upper and lower jaws do not align correctly. This misalignment can lead to several dental issues such as tooth decay, gum recession, and loss of adult teeth. In this article, we will discuss the various causes of a crossbite and how to prevent it.
Understanding the causes of a crossbite can help individuals make informed decisions about their oral health and reduce the risk of developing this dental condition.
Genetics and Developmental Abnormalities
Crossbites are a type of malocclusion that occurs when the upper teeth sit inside the lower teeth when the jaw is closed. This condition is often hereditary and can begin to develop at a young age. People with a family history of crossbites are more likely to develop this condition themselves, especially if there are other developmental abnormalities present in their family history.
However, crossbites can also be caused by injuries or accidents, so it’s important to consider all possible causes when diagnosing and treating them. Genetics play a crucial role in the development of crossbites, which is why a comprehensive understanding of family history is often necessary to create an effective treatment plan.
Early intervention is key to preventing the long-term consequences of untreated crossbites, such as gum recession, tooth decay, and even tooth loss. By identifying the underlying genetic and developmental abnormalities that lead to crossbites, dental professionals can help patients achieve a healthy and beautiful smile.
Habits Such as Thumb Sucking or Tongue Thrusting
Habits like thumb-sucking or tongue-thrusting can lead to the development of a crossbite, a malocclusion where the upper teeth sit inside the lower teeth. These habits can also affect the development of the mouth and jaw bone structure, causing misalignment and jaw pain.
Fortunately, breaking these habits can prevent the development of a crossbite. Practical methods include replacing the behavior with a different soothing technique, such as hugging a stuffed animal or blanket, using socks or band aids on the hands to make thumb-sucking uncomfortable, and creating a reward system for not engaging in the habit.
It’s important to address these habits early on in childhood to prevent long-term difficulties. If left untreated, a crossbite can lead to tooth decay, gum recession, and even tooth loss. Consulting with a pediatric dentist or orthodontist can help determine the best treatment plan for correcting a crossbite and ensuring a healthy bite and proper jaw growth.
Injury or Accidents That Affect Tooth Alignment or Jaw Growth
Injury or accidents can have a profound impact on the development of the teeth and jaw, leading to serious alignment issues such as crossbites. Facial trauma, jaw fractures, and dental injuries are all common injuries that can affect the growth and alignment of the teeth and jaw.
Facial trauma, such as being hit in the face, can cause the teeth to shift out of their natural position, leading to a crossbite. Similarly, jaw fractures can impede the normal growth of the jaw, which can cause misalignment issues as the permanent teeth come in. Dental injuries, such as losing a tooth or having an improperly placed filling, can also disrupt the proper alignment of the teeth and jaw, leading to crossbites.
When an injury or accident occurs, the natural development of the teeth and jaw can be disrupted, leading to serious alignment issues. As a result, it is important to seek prompt dental treatment anytime an injury or accident occurs to minimize any negative impact on the growth and alignment of teeth. Early intervention can ensure a healthy and properly aligned smile.
Treatment Options for a Crossbite
A crossbite is a type of malocclusion where the upper teeth fit inside the lower teeth when biting down. This condition can lead to a variety of oral health problems, such as tooth decay, gum recession, and jaw pain, if left untreated.
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to correct a crossbite, from traditional braces to oral appliances, and even jaw surgery. In this article, we will explore the different treatment options for crossbites, their benefits, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
Orthodontic Treatment with Braces or Invisalign®️
Orthodontic treatment is the most effective solution for correcting a crossbite. Both traditional braces and Invisalign®️ can be used to align teeth and jaws properly, thus fixing a crossbite.
Traditional braces apply constant pressure to teeth, forcing them to move into the correct position over time. Elastic rubber bands are often used in conjunction with braces to apply the required force to move the teeth. Invisalign®️, on the other hand, uses clear, removable aligners that gradually move teeth into position over time.
When it comes to correcting crossbites, braces offer more control over tooth movements and jaw alignment. Rubber bands are a common part of the treatment plan with braces, as they help to align the teeth and jaws properly. Invisalign®️, on the other hand, may not be as effective in correcting severe crossbites. However, for minor cases, Invisalign®️ can be a great alternative to traditional braces.
During the orthodontic treatment, it is common to experience mild discomfort or soreness. Patients need to maintain good oral hygiene and ensure regular dental checkups to prevent tooth decay. With a proper treatment plan and guidance from a skilled orthodontist, patients can achieve a healthy bite and a beautiful smile.






